Applications of Sealing and Solder Glass Frits
SCHOTT sealing glasses perform with reliable efficiency in a range of industrial operations, including fuel cells, batteries, vehicle combustion systems, electrical equipment, and components in the chemical and nuclear sectors. Solder glasses are used in MEMS packaging, opto-electronics, and display device sealing.
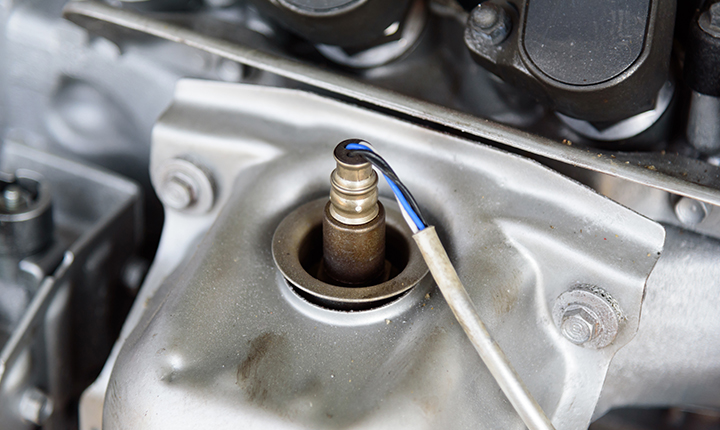
Corrosive Environments
Low-Temperature Joining
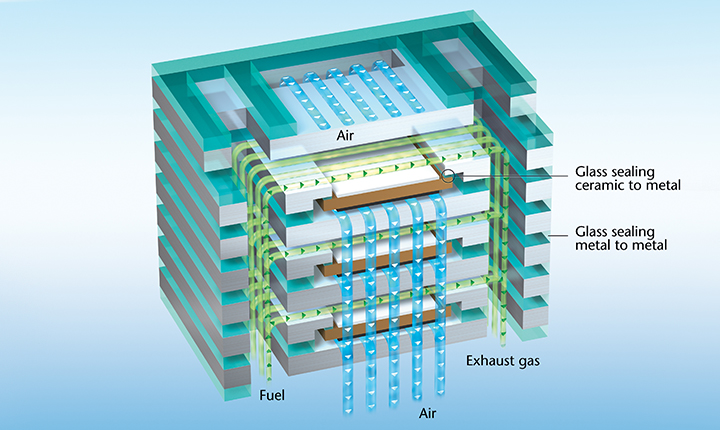
Solid Oxide Fuel Cells (SOFC) and Electrolyzer Cells (SOEC)
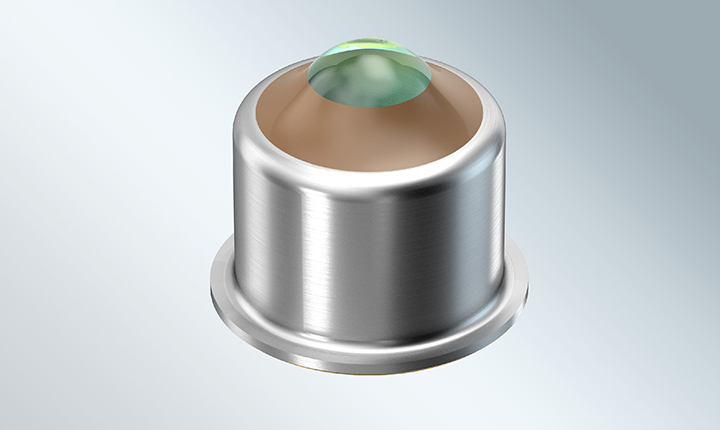
Sensor Technology

Weston Wright
Product Sales Manager