Technical Details of BOROFLOAT®
A highly valued portfolio of properties
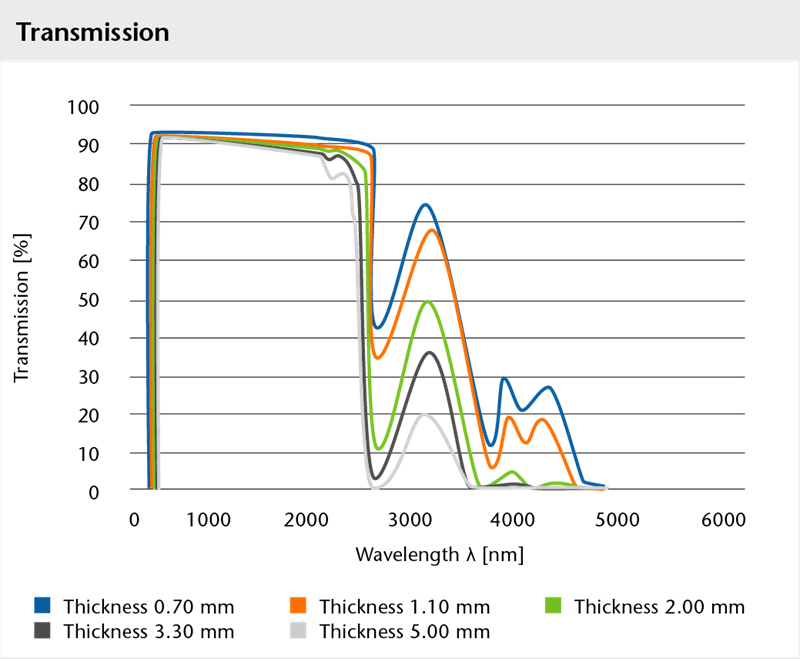
Thicknesses and dimensions
Standard thicknesses
| Thickness (mm) | Tolerance (mm) |
|---|---|
| 0.70 | ± 0.05 |
| 1.10 | ± 0.05 |
| 1.75 | ± 0.05 |
| 2.00 | ± 0.05 |
| 2.25 | ± 0.05 |
| 2.75 | ± 0.10 |
| 3.30 | ± 0.20 |
| 3.80 | ± 0.20 |
| 5.00 | ± 0.20 |
| 5.50 | ± 0.20 |
| 6.50 | ± 0.20 |
| 7.50 | ± 0.30 |
| 9.00 | ± 0.30 |
| 11.00 | ± 0.30 |
| 13.00 | ± 0.30 |
| 15.00 | ± 0.40 |
| 19.00 | ± 0.50 |
| 20.00 | ± 0.70 |
| 21.00 | ± 0.70 |
| 25.40 | ± 1.00 |
Panel thickness is continuously measured during production using laser thickness measuring equipment.
Further thicknesses and tolerances are available on request.
Standard sizes
| Size | Thickness |
|---|---|
| 1,150 x 850 mm | 0.7 – 25.4 mm |
| 1,700 x 1,300 mm | 19.0 – 21.0 mm |
| 2,300 x 1,700 mm |
3.3 – 15.0 mm |
Standard sizes of BOROFLOAT® 33
Thermal
Thermal properties
- Specific heat capacity cp (20–100 °C): 0.83 kJ/(kg·K)
- Thermal conductivity λ (90 °C): 1.2 W/(m·K)
- Transformation temperature Tg* (according to ISO 7884): 525 °C
Maximum Operating Temperature
- For short-term usage (< 10 h): 500 °C
- For long-term usage (≥ 10 h): 450 °C
The CTE of BOROFLOAT® 33 is 3 times lower than the CTE of Soda-lime glass.
Optical
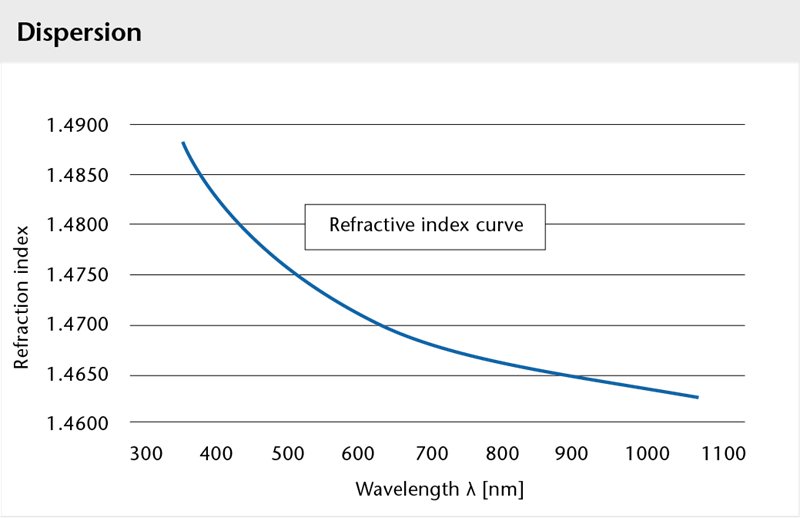
Optical index of refraction
| Wavelength λ (nm) | Refraction index n |
|---|---|
| 435.8 | 1.48015 |
| 479.9 | 1.47676 (nF’) |
| 546.1 | 1.47311(ne) |
| 589.3 | 1.47133 |
| 643.8 | 1.46953 (nC’) |
| 656.3 | 1.46916 |
Reference values, not guaranteed values.
Optical data
- Abbe number (ve = (ne – 1) / (nF‘ – nC‘)): 65.41
- Refraction index (nd (λ587.6 nm)): 1.47140
- Dispersion (nF – nC): 71.4 x 10-4
- Stress-optical coefficient (K): 4.0 x 10-6 mm2 N-1
Reference values, not guaranteed values.
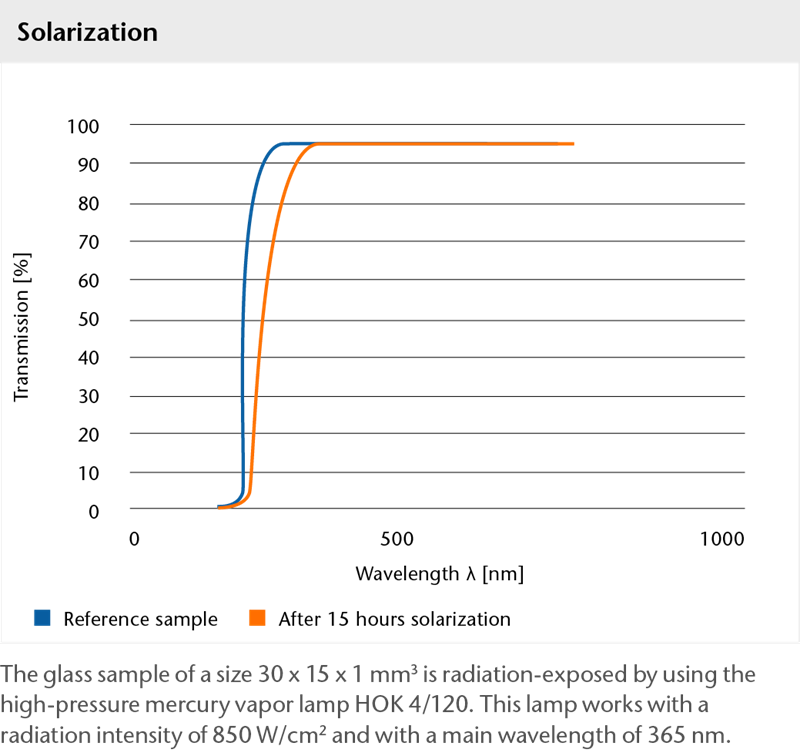
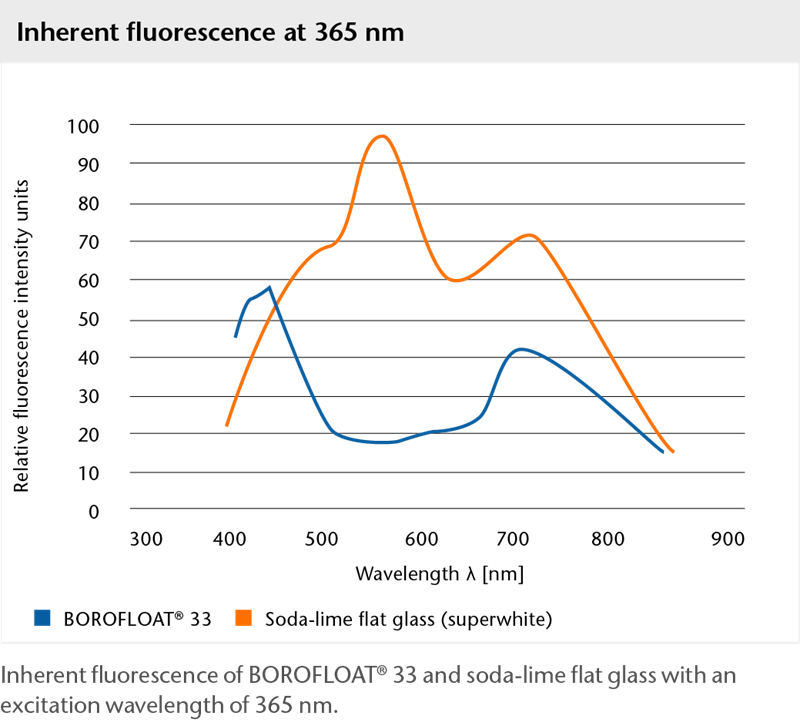
Inherent fluorescence
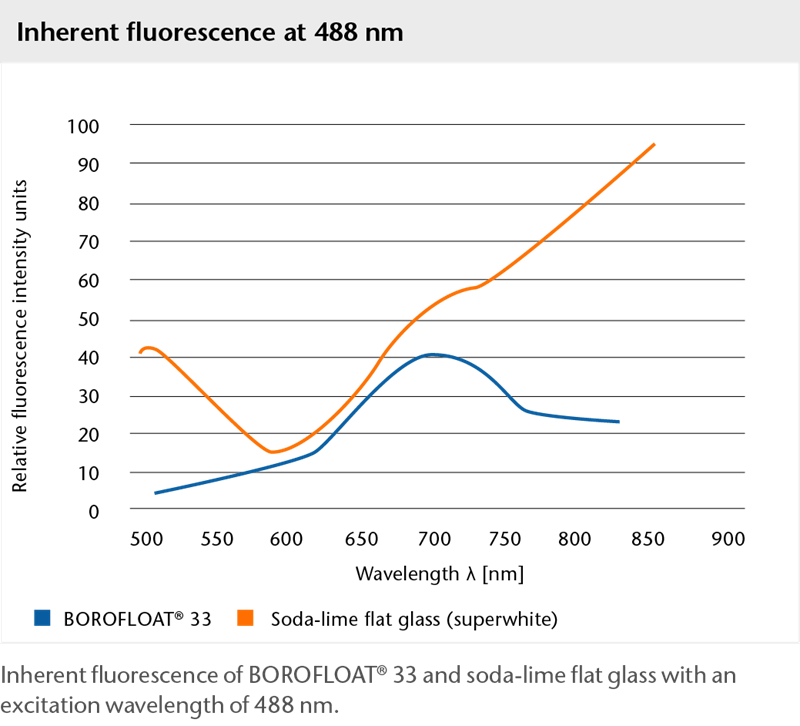
Chemical
Chemical durability
- Hydrolytic resistance (according to ISO 719 / DIN 12 111): HGB 1
- Hydrolytic resistance (according to ISO 720): HGA 1
- Acid resistance (according to DIN 12 116): 1
- Acid resistance (according to ISO 1776): ≤ 100 μg Na₂O per 100 cm²
- Alkali resistance (according to ISO 695 / DIN 52 322): A 2
Resistance to selected chemicals
24 h at 95 °C:
| Reagent | Abrasion [mg/cm2] | Visual observations |
|---|---|---|
| H20 | < 0,01 | Unchanged |
| 5 Vol.% HCl | < 0,01 | Unchanged |
| 0,02 n H2S04 | < 0,01 | Unchanged |
6 h at 95 °C:
| Reagent | Abrasion [mg/cm2] | Visual observations |
|---|---|---|
| 5 % NaOH | 1,1 | White stains |
| 0,02 n NaOH | 0,16 | White haze |
| 0,02 n Na2CO3 | 0,16 | Unchanged |
20 min. at 23 °C:
| Reagent | Abrasion [mg/cm2] | Visual observations |
|---|---|---|
| 10 % HF | 1,1 | Stained white haze |
| 10 % NH4F x HF | 0,14 | Unchanged |
Chemical resistance of BOROFLOAT® 33 to selected reagents as a function of time and temperature.
Quantity of Na2O released from BOROFLOAT® 33 compared tosoda-lime glass depending on the temperature after 16 hours.
Compared to soda-lime glass, BOROFLOAT® 33 has a significantly higher hydrolytic resistance, because the number of sodium ions in the glass network is significantly lower with BOROFLOAT® 33. The few sodium ions are also more strongly bound.
Mechanical
Mechanical properties:
- Density ρ (25° C): 2.23 g/cm3
- Young´s Modulus E (according to DIN 13316): 64 kN/mm2
- Poisson's Ratio μ (according to DIN 13316): 0.2
- Knoop Hardness HK0.1/20 (according to DIN ISO 9385): 480
Vickers-Test
Mechanical resistance to penetration by a pointed object – BOROFLOAT® 33 is particularly resistant due to its glass structure.
PEI Abrasion Test
Transition from sliding abrasion to erosion (grain fill, loose grains) – BOROFLOAT® 33 is particularly abrasion resistant.

