
Glass: a multifaceted sustainability champion
Climate change is one of the greatest challenges of our time. Individuals and companies are trying to reduce their carbon footprint, live and act more sustainably. Specialty glass is helping: from smart windows to efficient induction cooking to next-generation batteries – glass is the driving force behind numerous developments for the future. An overview of climate-friendly applications for this versatile material.
Glass is a valuable resource in the quest for sustainability.
- Specialty glass has increasingly become a helpful tool in enabling people to live more sustainable lifestyles and conserve resources.
- Whether in refrigeration in supermarkets, longer range electric vehicles, cooking surfaces with glass-ceramic, satellites with solar power or smart windows in architecture: specialty glass has an important contribution in a number of energy efficient technologies.
- With its diverse applications, multifaceted glass is proving to be a true sustainability champion.
"Germany has used up its resources for 2023," headlined SPIEGEL on May 4, 2023, referring to Germany's Earth Overshoot Day. According to calculations by the Global Footprint Network, that is the date that Earth’s natural resources would be depleted if everyone on the planet lived as Germans do. Put another way: if all countries consumed as many natural resources and produced as many emissions-per-inhabitant as Germany, it would take about three Earths. The global Earth Overshoot Day, which fell on July 28 last year, should be a serious wake-up call for society to use existing resources more sustainably.
With that in mind, specialty glass has increasingly become a helpful tool in enabling people to live more sustainable lifestyles and waste fewer resources. When shopping in the supermarket, for instance, specialty glass is used to keep the cold air inside the chiller cabinets. When we cook, we encounter it as an energy-efficient glass-ceramic cooktop. And in our electric cars, it can be found as glass powder installed in modern batteries that enable long distances on a single charge. And while producing that glass is certainly energy-intensive, ambitious researchers have been working on even more energy-efficient production processes that utilize green electricity and hydrogen.
To further understand how glass is a multifaceted material that provides more sustainable options, here are five examples of how glass is helping us live more sustainable today.
Shopping: Less electricity needed in supermarkets
A lesser-known aspect of shopping is that supermarkets are real power-guzzlers. Consider the fact that one store requires up to ten times more energy than a single household. Most of this power usage is due to the refrigeration units, which can take up almost half of a supermarket's total energy consumption. Why does food refrigeration require so much energy? Largely due to the simple fact that most chiller cabinets in the supermarket are not closed. On one hand, this allows shoppers to easily inspect and choose the food they want, but on the other hand, the chillers have to run constantly to keep the food cold.
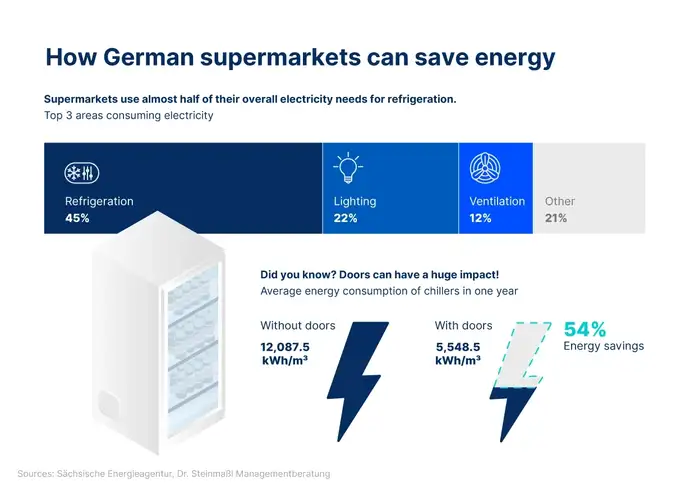
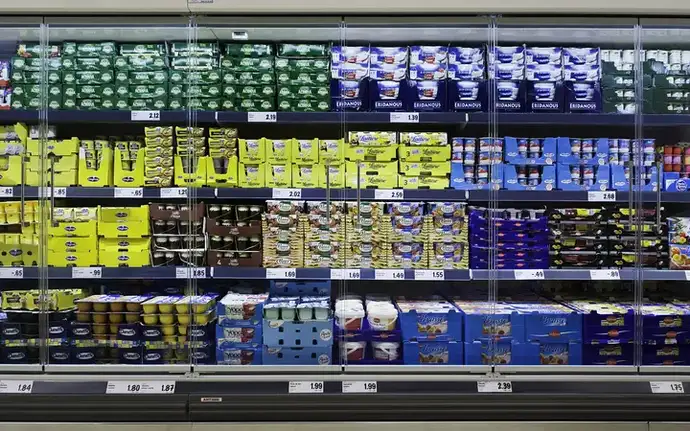
Glass door systems make chiller cabinets more efficient
Termofrost® offers a combination of robustness, durability, and high merchandise visibility for various new and retrofitted chiller cabinets. With frameless designs that offer a clear view to the goods and a sleek design, stores can be modernized in a short period of time. The product promises potential energy savings of up to 65% over conventional chiller cabinets.
Learn more about our glass door systems

Mobility: More range for electric cars
So, you just bought your groceries and need to get your produce back home and into your refrigerator as quickly as possible. If not on foot or by bike, an electric vehicle (EV) is the next best alternative. The popularity of electrically powered vehicles has grown consistently, with some estimates expecting 72% of all cars sold worldwide to be electric by the year 2040. One argument for accelerating the adoption of battery-electric vehicles is to develop more powerful batteries that boast longer ranges per charge. All over the world, various institutes and teams are researching new technologies to improve the range of electric cars – specialty glass plays an important role here, too.
At the moment, lithium-ion batteries are standard equipment in many EVs because of their performance. But the competition is catching up: solid-state batteries offer advantages in terms of range, while sodium-ion batteries are more cost-efficient. But where does glass fit into the equation? In solid-state batteries, glass powder serves as the electrolyte. This is an important component of all batteries, as it enables the flow of ions between the positive and negative terminals of the batteries. As such, glass can extend the life of lithium-ion batteries and increase their efficiency.
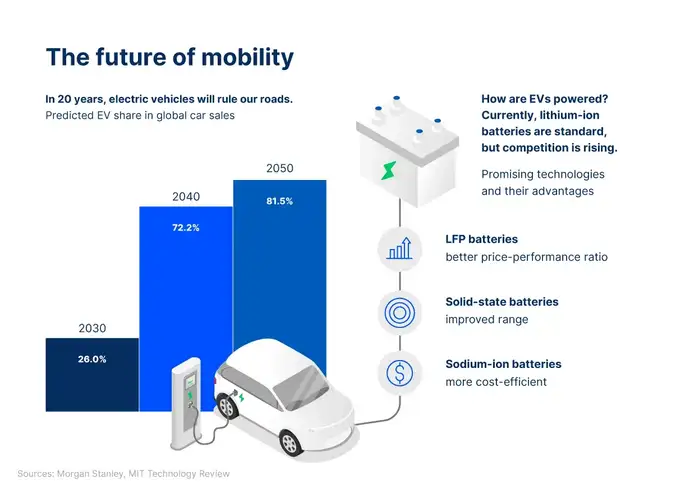
Specialty glass strengthens car batteries
SCHOTT developed a solution for extending the life of lithium-ion batteries. With the help of a special glass powder, it is possible to absorb harmful hydrofluoric acid, which is responsible for the decrease in the capacity of the cells. The powder binds fluorine, which protects the sensitive electrodes from acid.
Learn more about glass powder for batteries

Kitchen and household: energy-efficient cooking
Once you get home, you can quickly prepare a delicious meal with the groceries you bought. Once again, glass plays an integral part in making this aspect of life more sustainable. For instance, induction cooktops made of glass-ceramic are becoming increasingly popular worldwide. Not only do the stylish induction cooktops heat up quickly, but they're much more efficient and safer than other cooktop option on the market.
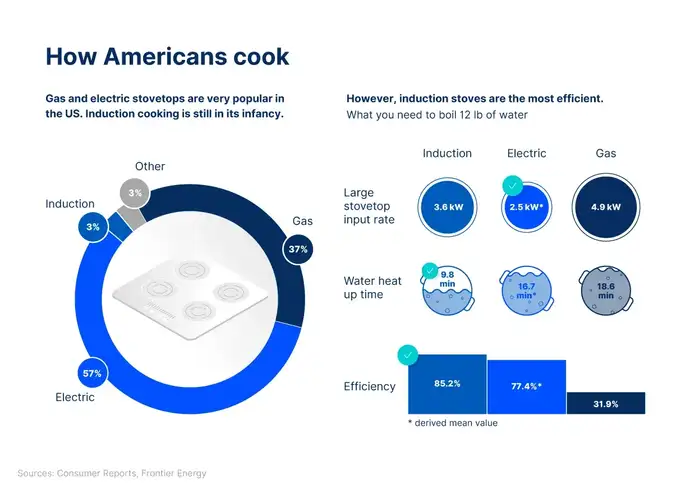
Sustainable cooking on glass-ceramic
CERAN® cooktops from SCHOTT have been trendsetters in kitchens worldwide for over 50 years. They are durable, robust, and resistant to strong temperature fluctuations. The inventor of black glass-ceramic for cooking has sold over 200 million cooktops to date, and even presented the next generation of the material in its anniversary year 2021. Luminoir® is translucent and, at the same time, jet black, thus creating new possibilities in product and lighting design for home appliance manufacturers despite its unchanging appearance. For users, the result is cooking surfaces that are intuitive and dynamic.
Learn more about CERAN® cooktops
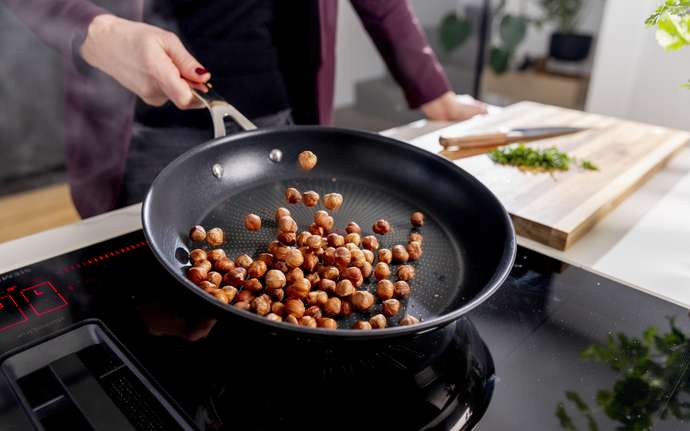

Communication: Solar energy for satellites
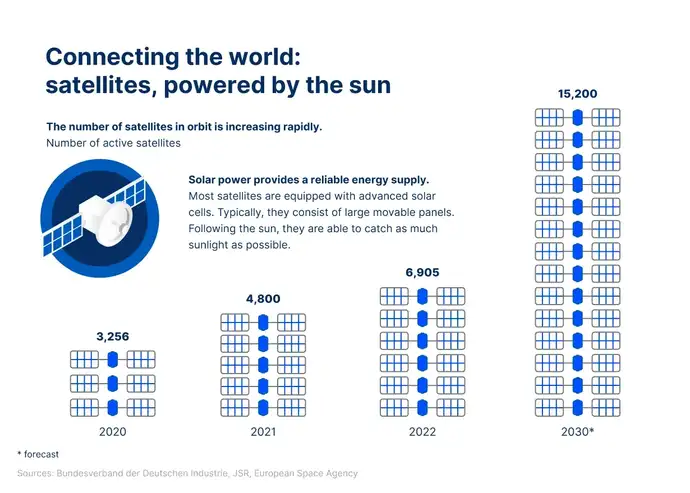
If you find yourself in the kitchen surrounded by groceries but still unsure what to cook, you can always turn to the internet to stream your favorite cooking show or peruse online recipes for inspiration. To do so, your phone must connect to the internet via satellites floating far above your house. Considering the world's hunger for data, it is unsurprising that the number of satellites in orbit around the Earth has increased rapidly in recent years. In 2020, there were 3,256 satellites orbiting above. By 2022 that number doubled, and according to estimates, there will be 15,200 satellites in space by the year 2040. After all, satellites are a critical pillar of the global communications network, and specialty glass ensures that each one functions properly.
In short, specially designed photovoltaic modules are used to power satellites. These modules are well protected by glass and convert sunlight into electricity. On of the most crucial factors in satellite design is keeping it lightweight. A lightweight satellite offers cost-effective solutions for accessing space through reduced material and resource requirements. It enables more flexible launch options while reducing the risk of collisions through increased maneuverability. Therefore, thin, lightweight glass not only keeps the overall weight of the satellite down, but it also protects solar cells from external influences. This protection is also crucial to the satellites’ design, since they must continue to function in an increadibly harsh environment. Without adequate protection, a solar cell can quickly get damaged in the extreme conditions in space, and thus unable to function.
Glass in space
Wherever specialty glass is used, SCHOTT is not far away – and that includes outer space. SCHOTT Solar Cell Cover glasses come in various designs and offer specific technical properties for demanding environments. In addition, SCHOTT is involved in optimizing the performance of various other components of satellites – cameras or mirror substrates, for example.
Learn more about our Solar Cell Cover glasses

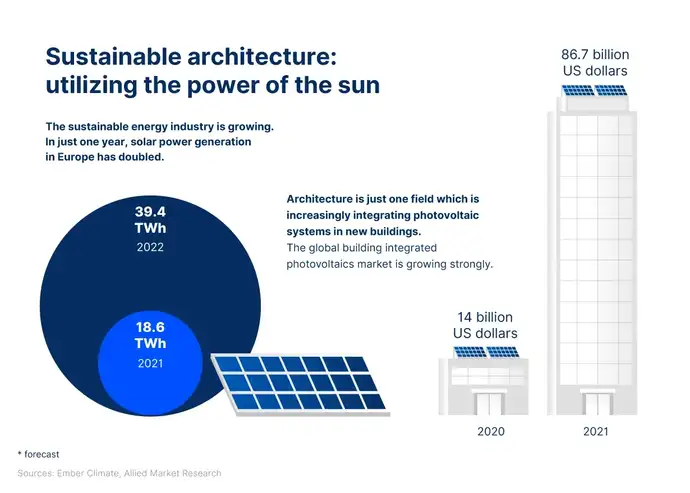
Living: Windows as solar power generators
A well-lit house with plenty of windows in very popular in architecture right now. The transparent material delights architects with a wide range of options for unusual designs that make the most of natural light. But specialty glass can do even more: In the same way the solar rays that hit roofs or facades are increasingly being converted into electrical energy by photovoltaic systems, solar rays that hit windowpanes can be converted as well. However, the latter has so far remained largely unused in home and building designs.
In fact, there are many ways that modern window systems can improve the energy efficiency of buildings. There are special privacy windows that switch from transparent to translucent and make blinds in buildings unnecessary. There are switchable windows that provide solar shading to help reduce energy costs, and energy-generating windows that use solar radiation to generate electricity. The company UbiQD has produced an exciting solution for the latter, as it inserts solar modules into window frames. Quantum dots, which are incorporated as an intermediate layer in the windowpane made of specialty glass, guide the incident light to the edge to the photovoltaic cells where it is converted into electricity.
Given the substantial number of windows installed in buildings around the world, this opens a whole new dimension for generating solar energy and shows that the potential of sustainable architecture for the future.
Smart windows thanks to specialty glass
Smart window systems require glass panes that provide good visibility and are lightweight, robust, and chemically resistant. BOROFLOAT® from SCHOTT combines these unique properties. It is the perfect partner for efficient window designs, especially due to its exceptional transmission properties in the UV, visible and near-infrared range, lightweight, and robustness against thermal and chemical environmental influences.
Learn more about BOROFLOAT®

These five examples show just a few of the applications where glass can help society make more sustainable choices. Specialty glass has long established itself as a versatile and innovative material, which is key in reducing the ecological footprint. In the fight against climate change and global challenges to sustainability, glass will undoubtedly continue to play a vital role. Because the facts are clear: Glass is not only a multifaceted material, but a sustainability champion as well.

