Technical Details of Radiation Shielding Glasses
With inner structural quality and internal transmission, SCHOTT's RD 30®, RD 50® and the RS Series deliver protection from radiation in challenging environments. They also offer protection against electrostatic discharge, while two of the glass types are resistant to solarization from ionizing irradiation.
Key strengths of SCHOTT Radiation Shielding Glasses
RD 30® and RD 50®
Technical data for RD 30®
Optical properties
Refractive index ne at 20°C (annealed at 40°C/h) 1.579
Light transmittance (d = 6.0 mm) 90.5%
Chemical properties
Hydrolytic class according to DIN ISO 719 HGB 3
Lead oxide content (PbO) ≥ 22%
Total heavy metal content ≥ 23%
Mechanical properties
Density in g/cm3 (as-delivered condition) ≥ 3.13
Other properties
Glass thickness 6.0 mm*
Evaluated sound insulation value Rw (C; Ctr ) = 34 (–2; –2) dB
* Sound reduction values for other thicknesses upon request.
Technical data for RD 50®
Optical properties
Refractive index nD at 20°C 1.79
Light transmittance (d = 5.0 mm) 85%
Chemical properties
Hydrolytic class according to DIN ISO 719 HGB 1
Lead oxide content (PbO) ≥ 65%
Total heavy metal content ≥ 70%
Mechanical properties
Density in g/cm3 (as-delivered condition) ≥ 5.05
Other properties
Glass thickness 8.1 mm*
Evaluated sound insulation value Rw (C; Ctr ) = 41 (–3; –3) dB
* Sound reduction values for other thicknesses upon request.
RD 50®: Lead equivalents in mm Pb for X-ray quality and maximum delivery dimensions
Minimum thickness d = mm |
Maximum thickness d = mm |
Attenuation equivalent in mm Pb at a tube voltage of: | Maximum weight kg / m2 |
Maximum dimensions mm x mm |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 80 kV | 100 kV | 110 kV* | 150 kV | 200 kV | ||||
| 5.0 | 7.0 | 1.5 | 1.5 | 1.5 | 1.5 | 1.4 | 35 | 2,400 x 1,220 |
| 7.0 | 9.0 | 2.1 | 2.1 | 2.1 | 2.1 | 2.0 | 45 | 2,400 x 1,220 |
| 8.5 | 10.5 | 2.6 | 2.6 | 2.5 | 2.5 | 2.4 | 53 | 2,400 x 1,220 |
| 10.0 | 12.0 | 3.1 | 3.1 | 3.0 | 3.0 | 2.9 | 61 | 2,400 x 1,220 |
| 11.5 | 14.0 | 3.5 | 3.6 | 3.5 | 3.5 | 3.3 | 71 | 2,400 x 1,220 |
| 16.0 | 19.0 | - | 5.0 | 4.9 | 4.9 | 4.6 | 96 | 1,500 x 1,220 |
| 20.0 | 23.0 | - | 6.3 | 6.1 | 6.1 | 5.8 | 116 | 1,500 x 1,220 |
RD 50®: Lead equivalents in mm Pb for radionuclides
Nuclide |
Attenuation equivalent in mm Pb with a thickness d of: | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4.0 mm | 5.0 mm | 7.0 mm | 8.5 mm | 10.0 mm | 11.5 mm | 16.0 mm | 20.0 mm | |
| C-11, N-13, O-15, F-18 | 1.4 | 1.8 | 2.6 | 3.1 | 3.7 | 4.2 | 5.9 | 7.4 |
| Co-58 | 1.6 | 2.0 | 2.8 | 3.4 | 4.0 | 4.6 | 6.4 | 7.9 |
| Co-60 | 1.7 | 2.2 | 3.1 | 3.7 | 4.4 | 5.1 | 7.1 | 8.9 |
| Fe-59 | 1.7 | 2.2 | 3.1 | 3.7 | 4.4 | 5.1 | 7.0 | 8.8 |
| Tc-99m | 1.1 | 1.4 | 2.0 | 2.4 | 2.9 | 3.3 | 4.6 | 5.7 |
Forms of supply for RD 30®
| Glass type | Thickness | Tolerance | Minimum lead equivalent at 56 kV | Maximum sheet dimensions |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Monolithic glass | 6.0 mm | +/- 0.25 mm | 0.5 mm Pb | 2,350 mm x 1,500 mm |
| Laminated glass | 2 x 3.1 mm | +/- 0,5 mm | 0.5 mm Pb | 2,400 mm x 1,300 mm |
| Toughened safety glass | 6.0 mm | +/- 0.25 mm | 0.5 mm Pb | 2,350 mm x 1,500 mm |
RD 30®: Lead equivalents in mm Pb and delivery dimensions
| Thickness d = mm |
Attenuation equivalent in mm Pb at a tube voltage of: | Max. weight kg / m2 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 50 kV | 56 kV | 76 kV | 80 kV | 110kV | 150 kV | ||
| 6.0 ± 0.25 | ≥ 0.5 | ≥ 0.5 | ≥ 0.5 | ≥ 0.5 | ≥ 0.5 | ≥ 0.5 | 20 |
Disinfection of radiation shielding glass
- Only use water, a mild detergent and a soft cloth.
- RD 30® can be disinfected using commercially available disinfectants that SCHOTT has approved. Disinfection using ultraviolet irradiation is also possible.
- Radiation Shielding Glasses should never be exposed to moisture or temperature fluctuations in conjunction with moisture and acidic air.
- Only use a sealant that is free of acids and alkaline substances (e. g. acetic acid, ammonia) during installation. Adhesive labels can cause discoloration if the adhesive reacts with the glass surface.
Protection meets an almost reflection-free view
RD 30® and RD 50® are also available in combination with the anti-reflective glass SCHOTT AMIRAN®. This laminated glass ensures the well-known protection against radiation and provides a clear view especially in the examination area.
RS Glass Series
Characteristics of Radiation Shielding Glasses
| General Characteristics | RS 253 | RS 253 G18 | RS 323 G19 | RS 360 | RS 520 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Minimum density ρ [g/cm³] | 2.5 | 2.52 | 3.26 | 3.6 | 5.18 |
| PbO – content [weight-%], synthesis | 0 | 0 | 33 | 45 | 71 |
| CeO2– content [weight-%], synthesis | 0 | 1.8 | 1.8 | 0 | 0 |
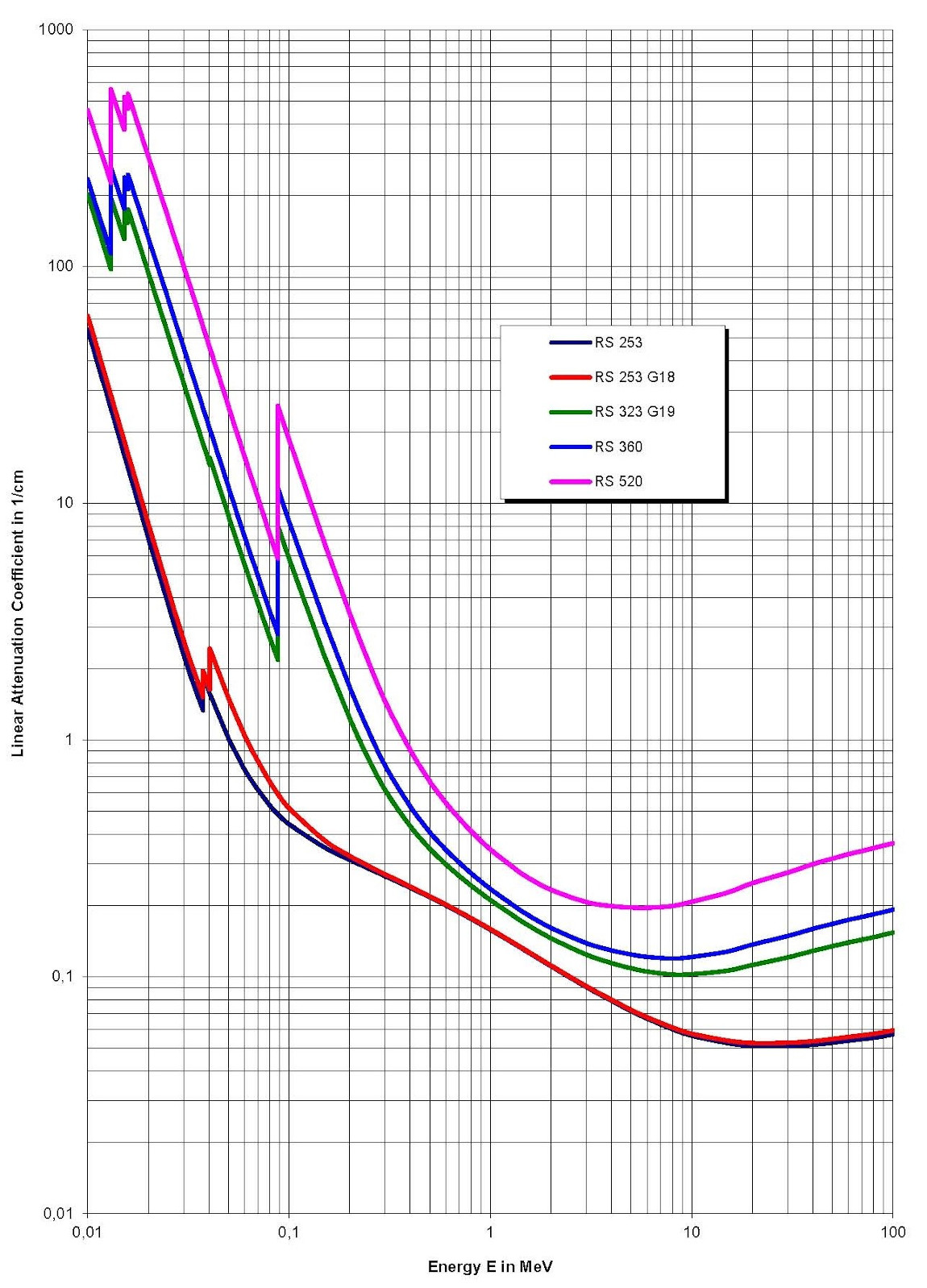
| Linear attenuation coefficients [cm–1] | RS 253 | RS 253 G18 | RS 323 G19 | RS 360 | RS 520 |
| E = 0.2 MeV | 0.32 | 0.33 | 1.25 | 1.72 | 3.54 |
| E = 0.662 MeV (137Cs) | 0.19 | 0.19 | 0.28 | 0.32 | 0.5 |
| E = 1.25 MeV (60Co) | 0.14 | 0.14 | 0.18 | 0.21 | 0.3 |
| Pb – equivalents | RS 253 | RS 253 G18 | RS 323 G19 | RS 360 | RS 520 |
| E = 0.2 MeV | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.11 | 0.16 | 0.32 |
| E = 0.662 MeV (137Cs) | 0.16 | 0.16 | 0.24 | 0.27 | 0.42 |
| E = 1.25 MeV (60Co) | 0.22 | 0.22 | 0.29 | 0.32 | 0.46 |
| Application limits | RS 253 | RS 253 G18 | RS 323 G19 | RS 360 | RS 520 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| with respect to discoloration, total dose [Gy] | - | 1 × 108 | > 1 × 108 | - | - |
| with respect to discharge, total dose [Gy]* | 1 x 103 | 1 × 108 | > 1 × 108 | 1 x 103 |
1 x 103 |
* discharge threshold (induced discharge)
| Optical Characteristics | RS 253 | RS 253 G18 | RS 323 G19 | RS 360 | RS 520 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Refractive index nd | 1.52 | 1.52 | 1.59 | 1.62 | 1.81 |
| Dispersion nd | 64.2 | 63.5 | 39.9 | 36.4 | 25.4 |
| Residual reflection loss per surface [%] | 4.25 | 4.25 | 5.1 | 5.6 | 8.3 |
| Internal transmission τi (100 mm) | RS 253 | RS 253 G18 | RS 323 G19 | RS 360 | RS 520 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| for λ = 546.1 nm | 0.987 | 0.895 | 0.88 | 0.992 | 0.984 |
| for λ = 589.3 nm | 0.985 | 0.925 | 0.925 | 0.993 | 0.985 |
| for λ = 632.8 nm | 0.981 | 0.941 | 0.94 | 0.99 | 0.981 |
For more detailed technical information on radiation shielding glasses, please contact our sales and application engineering teams.
Linear Attenuation Coefficients of SCHOTT Radiation Shielding Glasses
Supply Forms
- Finished blocks and plates: window faces visual grade polished, lateral faces ground
- Castings
Dimensions*
- max.size of finished slabs: 1600 x 1100 mm2 or 1360 x 1360 mm2
- max. weight: 1,300 - 2,000 kg/slab
* Larger dimensions and heavier weights upon request.
Material not available from stock, only customer-specific melts on request.
Quality Assurance
- 100% control of geometrical shape and internal quality.
- Parts are inspected during all stages of fabrication, including an intensive final inspection.
- The same quality inspection equipment is used as for optical glass.
FAQs
General / Introduction
|
1. What is the difference between RD 50® and RD 30®?
|
RD 50® and RD 30® have been given their product names based on their respective density of min. 5.05 g/cm³ or min. 3.13 g/cm³ and differ with regard to their applications, especially with regard to the protective effect, which is significantly higher with RD 50®.
|
|
2. How is this protective effect measured?
|
The protective effect is usually specified for the use of lead as a shielding material. For other materials such as glass, the protective effect is indicated as the lead equivalent, i.e. to which lead thickness the shielding effect of the material is equivalent.
|
|
3. Which lead equivalents correspond to RD 50® and RD 30®?
|
RD 50® offers lead equivalent values of 1.4 mm to 6.3 mm, depending on tube voltage and glass thickness. RD 30® offers a minimum lead equivalent of 0.5 mm Pb in 6 mm glass thickness.
|
|
4. Do RD 50® and RD 30® meet the necessary standards for your areas of application?
|
RD 50® meets the requirements of DIN EN 61331-2 and IEC 61331-2 for radiation protection in medical x-ray diagnostics. RD 30® is used for medical electrical devices built according to DIN EN 60601-2-45.
|
|
5. How is radiation protection achieved for e.g. BGW > 6.1 mm Pb?
|
By laminating two pieces of RD 50® glass together. The BGW adds up accordingly.
|
Planning and Installation
|
1. How are RD 50® and RD 30® installed properly? |
In any case, it must be ensured that the radiation protection on the wall side and the radiation shielding glass overlap to ensure full surface, continuous protection against radiation. Spaces without radiation protection may not be, i.e. no radiation protection material may be used 'butt to butt'. An overlap of the radiation protection materials must always be present.
|
|
2. How can a higher stability be achieved for movable elements (sliding door/wall)?
|
With laminated glass made of RD 50® with float glass on one or both sides (also tempered safety glass) to achieve a higher stability and/or surface protection of RD 50®.
|
|
3. Can RD 50® and RD 30® be processed into insulating glass?
|
Yes. It is only ever necessary to ensure that the radiation shielding glass is inserted on the room side. RD Glass must not be exposed to weather and environmental influences. We provide appropriate supplier addresses (specialists) for complete radiation protection systems such as doors, windows, pulpits, rooms.
|
|
4. Can scratches on RD 50® be subsequently polished?
|
Each individual case needs to be reviewed, it depends primarily on the scratch depth.
|
|
5. Can RD 50® and RD 30® be cut to size later (e.g. on site)?
|
In principle yes. However with RD 50®, care must be taken that the glass cutter is not ground too sharply and that only a little oil is used. The cut should always be made from the edge and should be broken as soon as possible. However, lead glasses should always be cut by an experienced glazier.
|
Maintenance and Usage
| 1. How can RD 50® and RD 30® be cleaned? What has to be considered? |
Please only use water, mild detergents and a soft cloth for cleaning so that the glass surface is not attacked.
|
|
2. Are there any cleaning agents suitable for RD 50® and RD 30®; sealants; disinfectants?
|
Yes, we can provide product names and manufacturers on request.
|
|
3. Can RD 50® and RD 30® burn?
|
No RD 50® and RD 30® are not flammable. The softening temperature of RD 50® is about 603°C and for RD 30® about 620°C.
|
|
4. How can RD 50® and RD 30® be disposed of?
|
According to federal, state or county regulations. Observe local regulations. The lead in the glass is chemically bound and cannot be leached out. Grinding and polishing residues are hazardous waste and must be disposed of in accordance with legal requirements.
|
