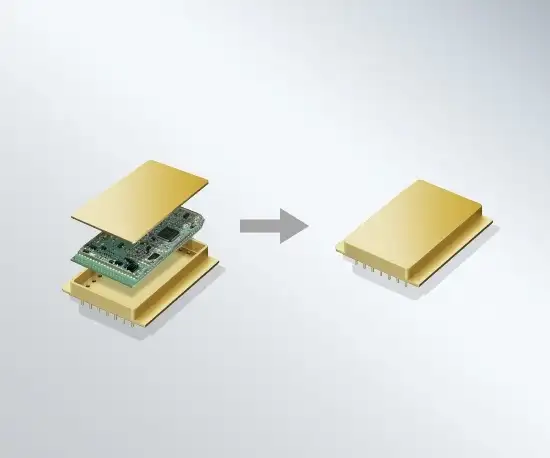
Glass-to-metal seals
Glass-to-metal sealing (GTMS) plays an integral role in electronic packaging. As a proven technology, it enables airtight, hermetic packaging for applications where performance, safety, and durability are crucial.
As the leading supplier of glass-to-metal seals, SCHOTT offers a broad portfolio that meets a wide range of demanding requirements. For over 80 years, we have been the partner of choice for customers worldwide, delivering innovative solutions tailored to specific needs.
Explore this page to learn more about glass-to-metal seals, their major applications, key product types and the technology and manufacturing processes behind GTMS.
What are glass-to-metal seals (GTMS)?
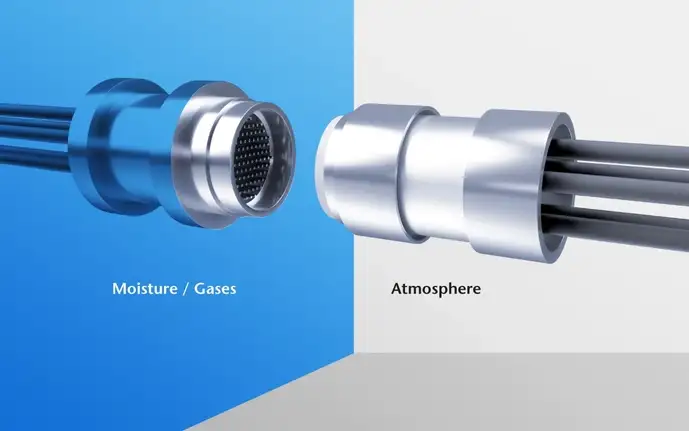
Hermetic glass-to-metal sealing technology combines metal and glass to create vacuum-tight electrical connectors, packaging, feedthroughs, or optical windows and lenses in electronics or electronic systems. Meeting requirements for harsh environments and high performance, hermetic GTMS are engineered to deliver uncompromised reliability.Glass-to-metal seal applications
Glass-to-metal seals are found in a vast array of products and industries, including:
-
high-temperature sensors
-
oil and gas applications
-
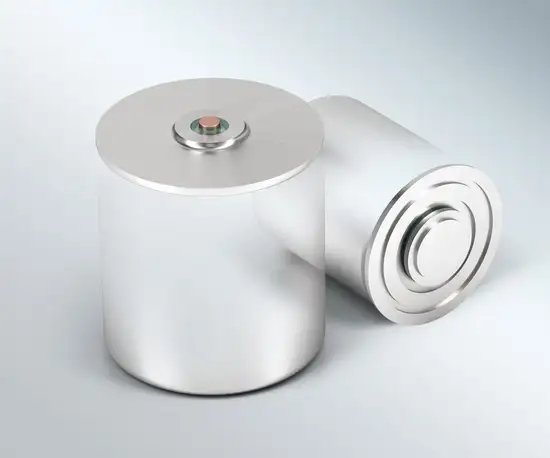
batteries and capacitors
-
nuclear reactors
-
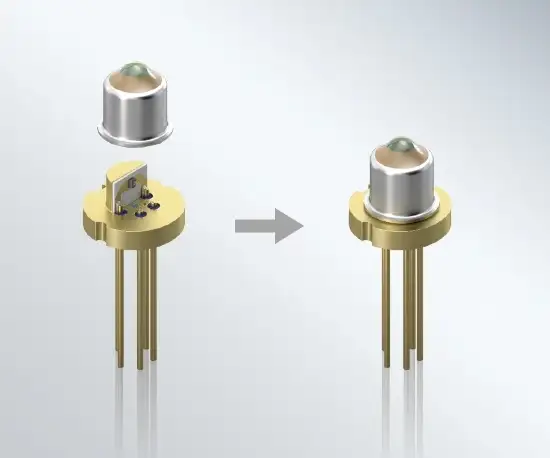
optoelectronic packaging
-
automotive airbags
The primary purpose for glass to metal seals is to reliably allow electrical or optical signals to pass through vacuum-tight housings or enclosures. However, these seals also serve the critical function of preventing moisture or gas intrusion and leakage that could cause damage or failure of the encapsulated electrical components and systems, semiconductors, electro-chemicals, pyrotechnics, or other substances.
By performing reliably in harsh operating conditions such as extreme temperatures, moisture, high pressures, or corrosive chemicals, GTMS technology facilitates longevity, performance, and efficiency improvements as well as innovative designs. At their core, these seals provide reliable connection and protection that enables the manufacture of high-quality and long-lasting hermetically sealed components or equipment. The versatility of this technology can be seen in the multitude of functions, designs, and sizes of GTMS components used in a broad range of applications.
Advantages: why GTMS can make the difference
Glass-to-metal seals are exceptionally versatile and can be engineered with customized features to meet requirements for specific application needs. Examples include:
Types of glass-to-metal seals
Hermetic glass-sealed components can be designed with a large variety of formats, sizes, material combinations, and degrees of complexity.
SCHOTT has GTMS products that range from 1.2 to 600 mm in diameter. Metals include stainless steel, aluminum, and titanium. Our experts know how to select the right combination of materials from hundreds of different glasses and metals.
Learn more about the different GTMS product categories.
Glass-to-metal sealing technology
One key aspect of creating high-quality glass-to-metal feedthroughs is combining materials with optimal coefficients of thermal expansion (CTE). The expert selection and subsequent processing of metals and suitable sealing glasses is essential for durable gas-tightness of the seal. GTMS products can be segmented into two types based on the glass and metal used and the ratio of their thermal expansions:
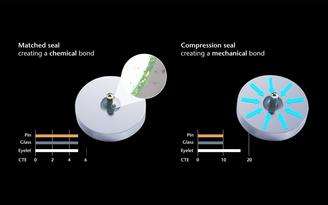
Matched seals
In matched seals, the CTEs of the glass and metal are balanced. This type of seal is typically used for applications where high-temperature variations are present or when tight pin pitch or dimensional requirements are factors (for example, miniaturized or non-round shapes). Depending on the design, matched glass-to-metal seals can maintain integrity through tens of thousands of heating and cooling cycles and are well suited for semiconductor and optoelectronic assemblies where structural integrity is essential for precise operation of the enclosed electronics.
Compression seals
Compression seals use glass and metal with vastly different CTEs. This causes the outer metal eyelet (housing) to shrink firmly onto the sealing glass during the production process. This compressive force forms a seal with immense bonded physical strength. In fact, the compressive strength of glass is 10 to 20 times higher than its tensile strength. This is why compression seals are typically used for designs that require high mechanical robustness. Examples can be found in automotive and energy applications, where long-term seal integrity is essential for continued safe operation of electronics in volatile environments.
How glass-to-metal seals are produced
Hermetic glass to metal seals are made using a complex but extremely effective production process involving just three components: the metal eyelet (housing), metal pins (feedthroughs), and a glass preform (sealing material). Achieving exceptional reliability of the final assembly requires a thorough understanding of the fundamental details. Competence in various glass types and formulations is key for maximizing robustness and reliability, especially for customized components. For maximum seal integrity, selecting the right metal and glass combination for the application and properly executing the sealing process are critical. SCHOTT’s in-house development capabilities give us the ability to alter or engineer entirely new glass types to solve unique challenges or enable new applications.
The manufacturing of glass-to-metal seals can be broken down into five main areas:
-
Choosing the right sealing glass
-
Packaging and feedthrough design and validation
-
Sealing
-
Plating
-
System integration
Production process
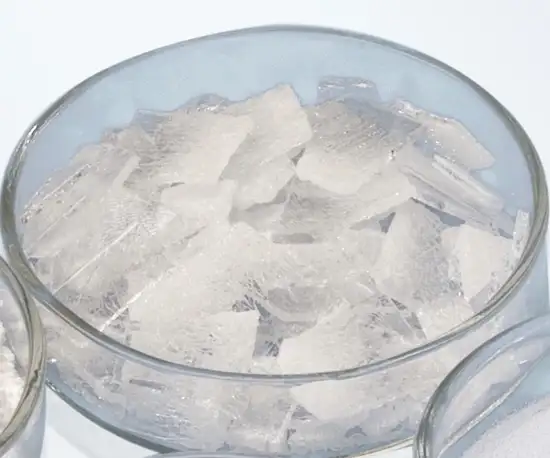
Choosing the right sealing glass
As a glass company at heart, glass expertise and manufacturing capabilities are the ‘secret ingredients’ that set SCHOTT apart in glass-to-metal sealing. Glass development, melting, milling, and preform manufacturing are all fully managed in-house by top glass formulation and hermetic sealing experts.
Choosing the right sealing glass based on the metal used and the operating conditions is essential for producing a highly durable glass to metal seal. SCHOTT offers the broadest range of standard glasses and continually develops new specialty glasses that can be used to meet advanced requirements. These capabilities enable us to meet the exact specifications our customers require.
To produce glass preforms, specialty glass melts are processed into shards, milled into fine glass powder, and then pressed and sintered into preforms. SCHOTT glass preforms have an extremely high dimensional accuracy, mechanical stability, consistent weight, and smooth surfaces – all aspects that play a decisive role in enabling robust and reliably hermetic GTMS.
Packaging and feedthrough design and validation
The development process at SCHOTT is collaborative: We closely work with our customers to deliver the best components for the application at hand.
Direct engineering support, complete customization, and rendering of more cost-efficient or less complex designs are all part of the design and development for glass-to-metal seals. SCHOTT can often improve on the original product concept by drawing on our experience and advanced validation measures.
Validation is key for GTMS. SCHOTT can perform simulations and tests with varying tools and support systems to verify successful implementation in applications and with customer processes. We offer welding, soldering, handling, and various other approaches to demonstrate proof of concept. The bottom line is we take your vision and make it work!
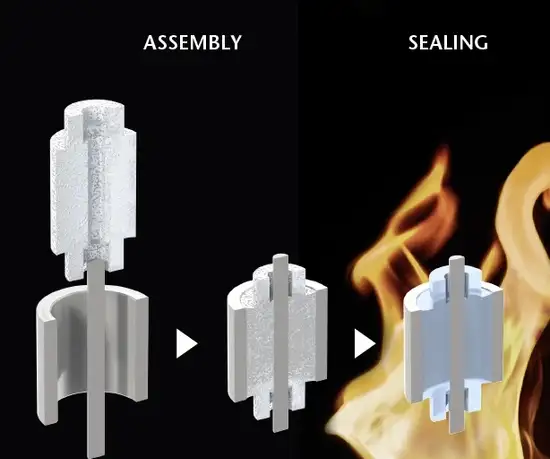
Sealing
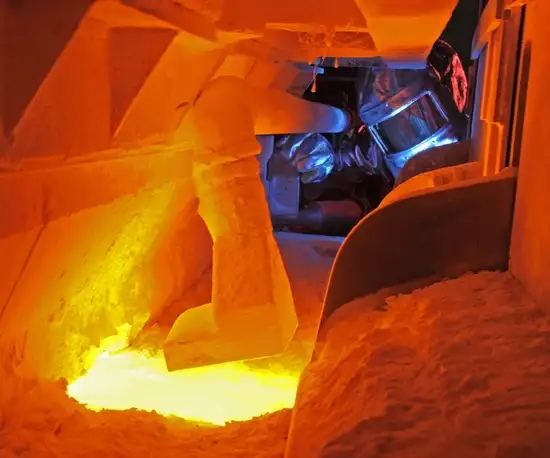
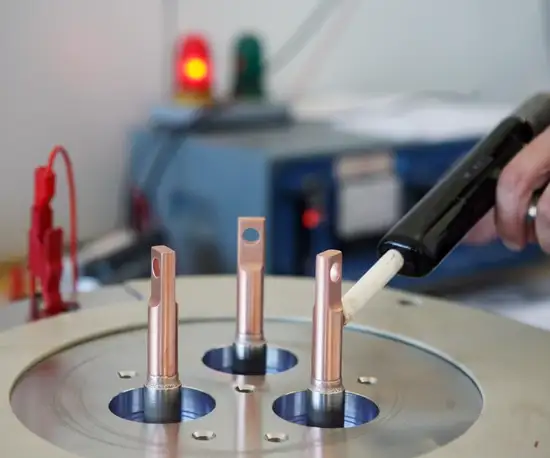
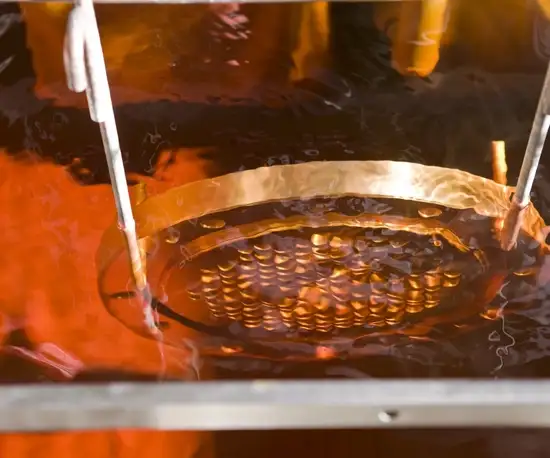
The sealing process transforms the three separate components into a single, vacuum-tight glass-to-metal sealed assembly. To do this, the glass preform, metal eyelet, and metal pins are assembled in a carbon fixture and put through a furnace in a highly controlled and specialized process. The temperature, oven conditions, gas compositions, and heating/cooling behavior of the materials are all expertly optimized to meet assembly requirements.
The end result of a successful glass to metal sealing process is a robust and durable component manufactured according to the exact established design specifications.
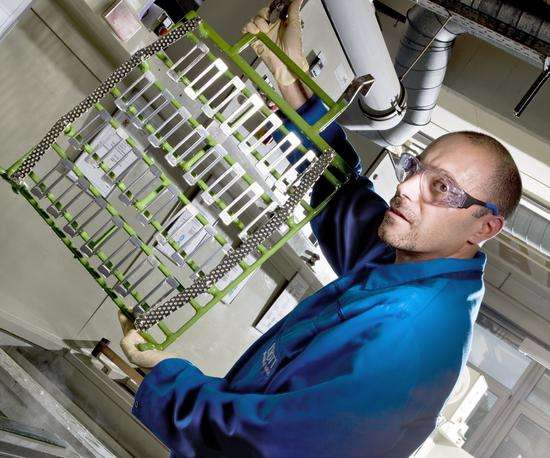
Plating
Plating, the final step of producing glass to metal seals, involves applying various surface treatments after the sealing process is complete. These treatments serve various functions such as corrosion protection or enabling electrical interconnection. Plating metals, such as nickel, gold, and zinc, are often applied only to the pins to save precious metal.
SCHOTT performs all plating processes in-house. This is a key differentiating factor in the production process as many GTMS manufacturers outsource this step, leading to longer lead times and potential quality issues.
The internal plating infrastructure at SCHOTT is optimized to enable both prototype quantities as well as high-volume serial production with consistent quality. We can advise on material types and thicknesses to optimize efficiency and performance for the final assembly.
System integration
After the glass to metal seals pass SCHOTT’s final quality inspection, they are shipped to the customers, who will then install the feedthroughs and connectors into their hermetic assembly.
Customers also equip headers and microelectronic packages with chips or PCBs, for example. Electrode or laser welding is used to bond the wires and close the housing.
The same applies for batteries and capacitors: After they are filled with the electrolyte, the customer welds the SCHOTT lid to the battery or capacitor can.
Customers can integrate the hermetic assemblies into their products themselves or commission a contract manufacturer to do this.
Discover recent application examples
Product portfolio
SCHOTT is the world leader in hermetic glass-to-metal seals (GTMS), serving a wide variety of applications that impact everyday life. Explore our top product offerings below or go to the Product Selector to view all products.
Want to talk directly to an expert?
Let’s discuss how glass-to-metal sealing can be a fit for your application.