Hydrogen is the key to a carbon-neutral future
Hydrogen is considered to be an alternative fuel and is playing a main role in decarbonization efforts across the world. As an industry-leading glass company, SCHOTT is actively contributing to climate protection by promoting the use of hydrogen and other green energy in the glass melting process. As a supplier, SCHOTT also offers innovative specialty glass for many hydrogen applications. Kristina Gruber, Project Manager Hydrogen at SCHOTT Electronic Packaging, shared with us some technology trends in the hydrogen industry and explained how specialty glass can improve safety and efficiency along the entire value chain.
Kristina Gruber is a member of the P2X4A Working Group of the VDMA (German Mechanical Engineering Industry Association) and Project Manager Hydrogen at the SCHOTT Electronic Packaging Division. She is dedicated to improving safety in the hydrogen value chain with SCHOTT's sealing technology.

From your perspective, what role will hydrogen play in the future?
From my perspective, low-carbon or green hydrogen plays a significant role in meeting CO2 emissions reduction requirements. Thanks to its extreme versatility, industry players use it in many sectors and applications. Some examples include using clean fuel to generate power or heat for feedstock in the chemical industry, and as a replacement for fossil fuels in the mobility area. Hydrogen has great potential to decarbonize so-called hard-to-abate sectors like steel or cement production, aviation, and shipping. These are highly energy-intensive sectors that will not achieve climate neutrality by energy efficiency alone, or for which electrification would be a tremendous challenge or not be possible at all.
Moreover, hydrogen has the great advantage that it can be stored in large amounts over long periods of time. That means it can also support the integration of fluctuating renewable energy types.
Low-carbon or green hydrogen is currently quite expensive because production quantities are still low. However, with rising quantities and increasingly efficient electrolyzers, production costs are expected to decrease considerably.

What is the significance of hydrogen for SCHOTT?
At SCHOTT, we are exploring the use of hydrogen for our production processes. We believe it could be one possible solution to becoming a carbon-neutral company.
SCHOTT is one of the leading specialty glass companies worldwide. Glass production requires a lot of energy – similar to companies in the plastics, steel, paper, and building materials industries. As material manufacturers, we are all at the beginning of the value chain. Specialty glass production is particularly energy intensive because it requires high melting temperatures of up to 1,700°C. Until now, we’ve heated our melting tanks with fossil fuels or electricity. Due to the high-energy demand, this results in a high carbon footprint.
However, we are working to change that. We take our social responsibility seriously and see it as our obligation to lead by example and actively contribute to climate protection. We’ve set a goal for ourselves to become the world's first climate-neutral specialty glass manufacturer by 2030. Using hydrogen as one potential energy source for our glass production reduces energy emissions and contributes to climate neutrality.

Is SCHOTT actively involved in the hydrogen value chain?
Yes, SCHOTT is exploring the use of hydrogen, but it is also a supplier of products for the entire hydrogen value chain.
As a hydrogen user, SCHOTT is involved in the Kopernikus project P2X (Kopernikus-Projekte: Kopernikus-Project: P2X), which is funded by the German Federal Ministry of Education and Research. This research project studies the most promising power-to-X technologies to help the transport, industrial, and heating sectors create low-emissions solutions. P2X technologies convert renewably generated electricity into other forms of energy, like fuels, heat, gases, or chemicals.
In 2021, our experts performed initial melting tests on laboratory scale with some promising results. That’s why we’re pursuing further research to learn more about the capabilities and limits of hydrogen in climate-friendly glass production.
However, developing these new melting technologies takes time and implementing them on a larger scale strongly depends on external factors, most importantly the availability of green hydrogen at competitive costs.
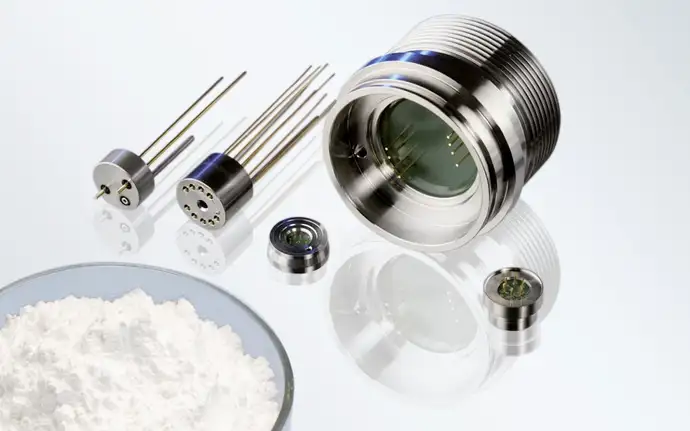
In addition, we have developed some innovative solutions for the hydrogen value chain spanning from generation to end use. For example, SCHOTT glasses have been used as sealing materials for solid oxide fuel cells (SOFC) since the 1990s. Our glass-insulated electrical penetrations are widely used to transport liquefied and compressed gases safely. Based on decades of expertise in the automotive industry, we’ve developed reliable sensor housing and feedthroughs for fuel cell vehicles. All these products help improve safety in the hydrogen industry.
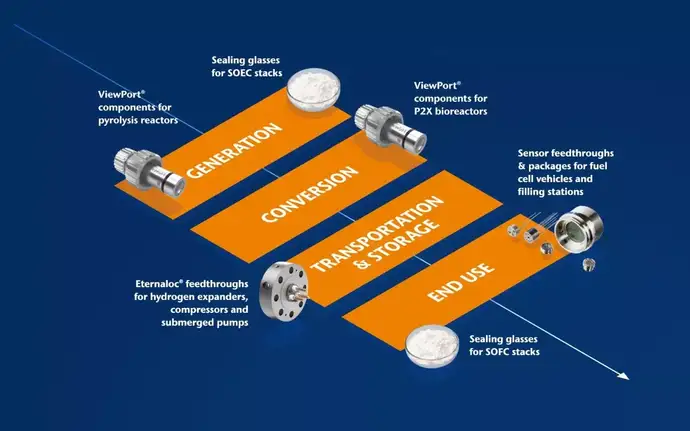
SCHOTT’s innovation solutions run the entire length of the hydrogen value chain.
What are SCHOTT’s core competencies as a supplier to the hydrogen industry?
All of our products for the hydrogen industry are based on our core technologies of hermetic packaging and specialty glass. As non-aging inorganic materials, glass powder and glass-sealed hermetic packaging can perform reliably in challenging conditions and harsh environments. These include high-pressure scenarios, extreme temperatures ranging from -253°C up to 950°C, and explosion risk. These qualities of inorganic glass materials improve the safety of the hydrogen value chain. In addition to the unique nature of the glass material itself, our innovative capabilities enable us to offer customized products well suited to fulfill the industry standards of the hydrogen sector.
We pay close attention to developments in the hydrogen industry, and we are committed to providing efficient and safety-oriented solutions. We want to continue helping establish hydrogen as a viable alternative energy in a number of sectors to achieve a climate-neutral future.

